Expert Knowledge
Textbook
130 pages know-how: Handbook of LED and SSL Metrology
Authors: Dr. Günther Leschhorn, Dr. Richard Young
Rapid developments in LEDs over the past decade have created a major growth market with completely new applications. These applications have placed increasingly stringent demands on the optical characterization of LEDs and Solid-State Lighting devices. Specific expertise is needed in order to achieve precise and reproducible results.
This handbook discusses the special characteristics of LEDs and emerging OLEDs. It provides an overview of state-of-the-art measurement equipment and gives recommendations for obtaining accurate measurement results.
»The “Handbook of LED and SSL Metrology” is a truly exciting work in that it crosses the need of a broad set of participants in the LED space. Newcomers to LED lighting can use the book to quickly develop a knowledge base while experienced industry participants will find ongoing value in the book as a constant technical reference on their bookshelf.« ─ Maury Wright, Editor-in-Chief, LEDs Magazine
»In this extensively updated edition of the “Handbook of LED and SSL Metrology”, the authors stay abreast of changes due to the introduction of LEDs. They explain, in a coherent way, all one needs to know about metrology in general as well as the specifics of SSL metrology. In short, it is a book every lighting specialist dealing with measurement should have on his or her bookshelf.« ─ Arno Grabher-Meyer, Editor-in-Chief, LED Professional Magazine
ISBN: 978-3-86460-917-6 (E-Book, 39.99 €)
ISBN: 978-3-86460-643-4 (Paperback, 40 €)
ISBN: 978-3-86460-644-1 (Hardcover, 78 €)

Available:
Glossary
Radiometric and photometric quantities
Note: Subscript "e" relates to "radiometric" and "v" to "photometric"
The V(λ) curve is used in photometry to convolute the radiometric quantity that is a function of the wavelength λ with the sensitivity function of the human eye in the wavelength range from 380 nm to 780 nm. The photometric quantity luminous flux Φv is then obtained by integrating radiant power Φe(λ) as follows:
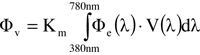
The unit of luminous flux Φv is the lumen [lm]. Factor Km = 683 lm/W establishes the relationship between the (physical) radiometric unit watt and the (physiological) photometric unit lumen. All other photometric quantities are also obtained from the integral of their corresponding radiometric quantity weighted with the V(λ) curve.